1.1- Fixed a problem that occurs on TI-89 HW v2.
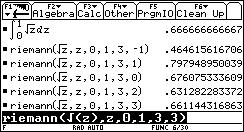
Riemann(Expr,IndependantVar,LowerLimit,UpperLimit,Partitions,Operation)
Expr: An integrable function.
IndependantVar: The independant variable.
LowerLimit: The lower limit of the approximation.
UpperLimit: The upper limit of the approximation.
Partitions: The number of partitions for the approximation.
Operation: The integer -1, 0, 1, 2, or 3, indicating one of the following operations:
-1 Riemann approximation at LEFT endpoints.
0 Midpoint Rule.
1 Riemann approximation at RIGHT endpoints.
2 Trapezoid Rule.
3 Simpson's Rule.
Note: Approximations with a large number of partitions can take quite some time if the calculator is set for either EXACT or AUTO. You can greatly speed up the process if you either set the calculator for APPROX or press [DIAMOND][ENTER] instead of just [ENTER].
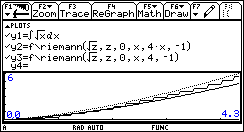
Graphing: The variable used in the first and second arguments (Expr, IndependantVar) cannot be the x variable. The figure shows an exact integral (y1=upper, dotted graph), the approximation at left endpoints calculated from 0 to x for each point with four partitions per unit of x (every 1/4x) (y2=middle, stepped graph), and the approximation at left endpoints calculated from 0 to x for each point with the interval 0 to x divided into four partitions (y3=lower, line graph).
Return value:
An approximation of the integral.
Examples:
1. Riemann(z1/2,z,0,1,3,-1)
Approximate the integral of z1/2
from 0 to 1 with 3 partitions using LEFT endpoints.
2. Riemann(z1/2,z,0,1,3,0)
Approximate the integral of z1/2
from 0 to 1 with 3 partitions using the Midpoint Rule.
3. Riemann(z1/2,z,0,1,3,1)
Approximate the integral of z1/2
from 0 to 1 with 3 partitions using RIGHT endpoints.
4. Riemann(z1/2,z,0,1,3,2)
Approximate the integral of z1/2
from 0 to 1 with 3 partitions using the Trapezoid Rule.
5. Riemann(z1/2,z,0,1,3,3)
Approximate the integral of z1/2
from 0 to 1 with 3 partitions using Simpson's Rule.